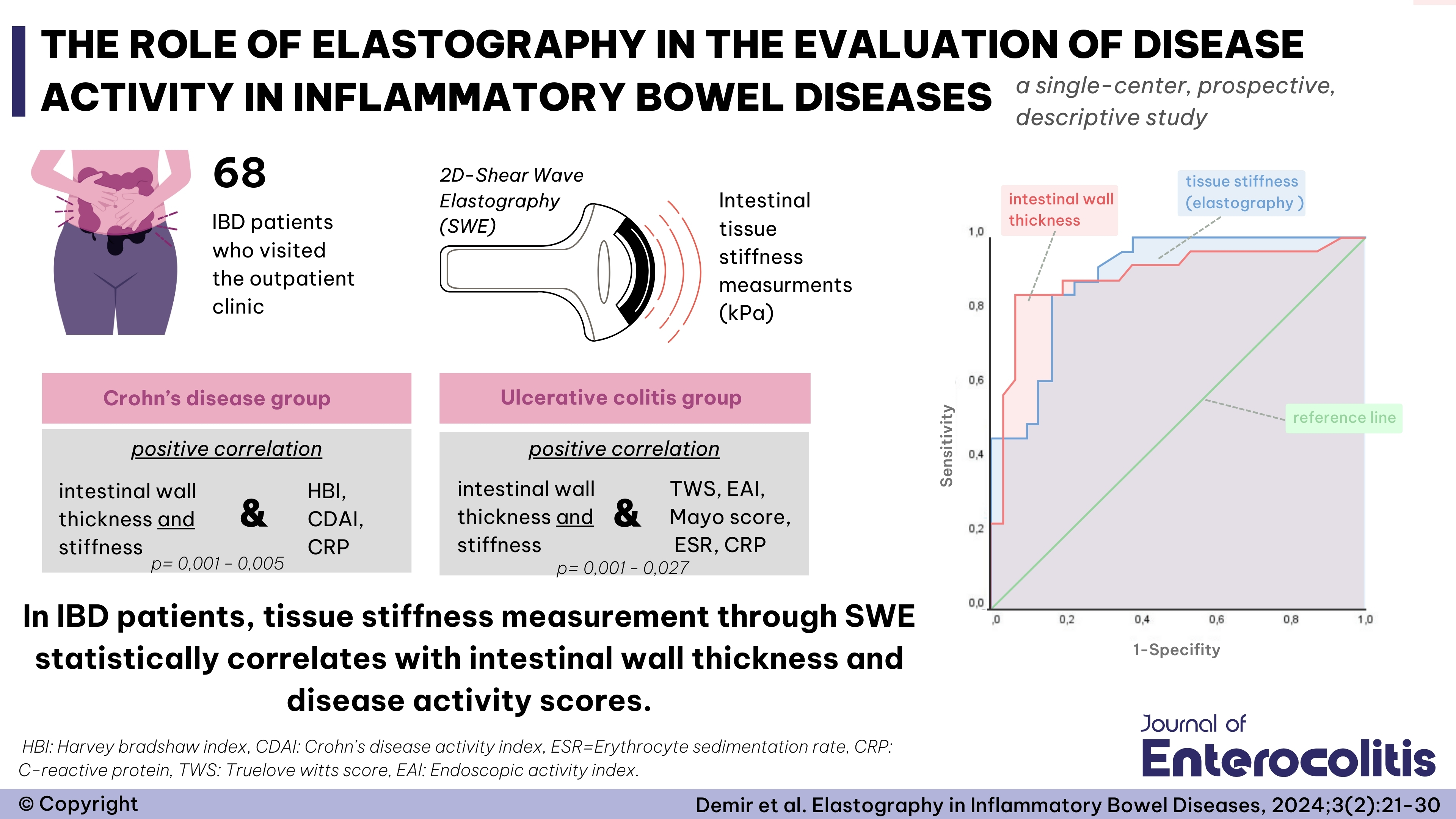
Abstract
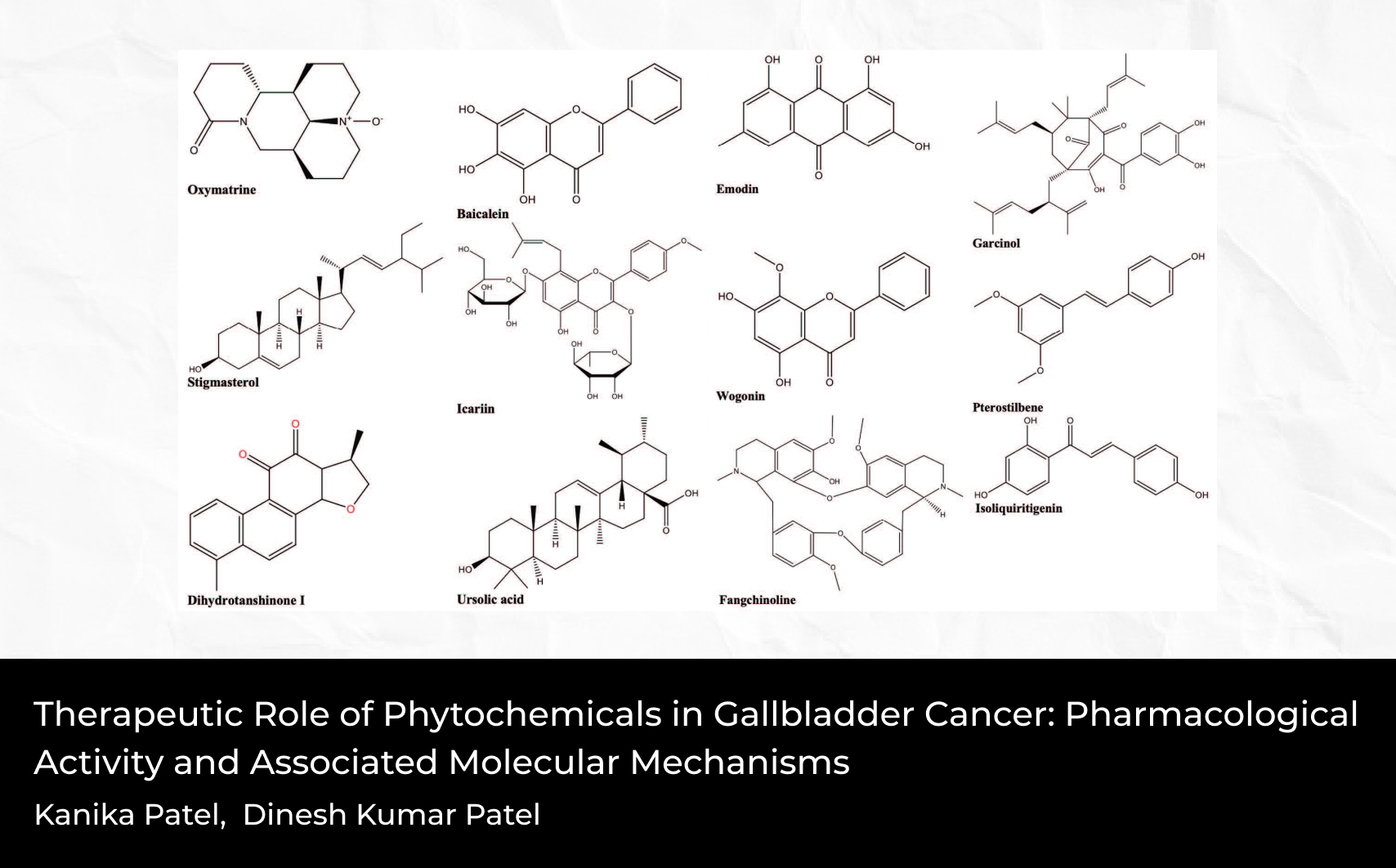
Gallbladder cancer (GBC) is a relatively rare but highly lethal malignancy. It is the most aggressive biliary tract carcinoma and the sixth most common gastrointestinal cancer worldwide. Over 90% of patients are diagnosed at an advanced stage due to the absence of symptoms in the early stages. The primary clinical treatment for GBC is surgical resection, while chemotherapy and postoperative radiation therapy can improve prognosis. This study compiles and analyzes scientific data from PubMed, Google Scholar, Google, Scopus, and ScienceDirect to evaluate the biological potential of phytochemicals in medicine and their efficacy in treating gallbladder cancer. Additional scientific evidence has been gathered from books, journals, and scientific reports to assess the therapeutic effectiveness of phytochemicals against GBC. This article also discusses the biological significance of gallbladder cancer in medicine. Scientific data analysis highlights the biological potential of numerous phytochemicals, including oxymatrine, baicalein, stigmasterol, icariin, dihydrotanshinone I, ursolic acid, emodin, garcinol, wogonin, pterostilbene, fangchinoline, isoliquiritigenin, cirsimaritin, ponicidin, oridonin, magnolol, and ginsenoside Rg3, in targeting gallbladder cancer. Additionally, this study examines the molecular mechanisms underlying their efficacy. Scientific analysis confirms the therapeutic potential of phytochemicals in GBC treatment. However, further research is needed to validate their clinical applicability, elucidate precise molecular mechanisms, and ensure their safety profiles.




 Kanika Patel1
Kanika Patel1