Abstract
In inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), surgery plays a crucial role in disease management, particularly when active disease cannot be controlled by medical therapy or when complications arise, especially in Crohn’s disease (CD).In ulcerative colitis, surgery is indicated for cases of acute severe colitis and chronic, treatment-refractory disease. Restorative proctocolectomy and rectal-sparing surgery are the preferred approaches in certain patient groups. In CD, surgery is typically performed either alone or in combination with medical therapy in the presence of strictures, fistulae, or penetrating disease.The timing of surgery and the performance of elective procedures under optimal conditions are critical to effective surgical management. During the perioperative period, patients should be optimized through measures such as nutritional support, while ongoing treatments (e.g., corticosteroids and anti-TNF therapies) should be carefully assessed. Elective surgeries are associated with fewer postoperative complications and higher success rates.Surgical options may include procedures like stricturoplasty and endoscopic balloon dilation for localized disease, as well as resection or diversion stoma for more severe cases.Although advancements in medical therapies have reduced surgical rates, the management of IBD still requires an individualized approach that integrates both medical and surgical strategies. A multidisciplinary treatment plan is essential to achieve optimal outcomes, particularly in complex cases involving perianal disease or fistulae.


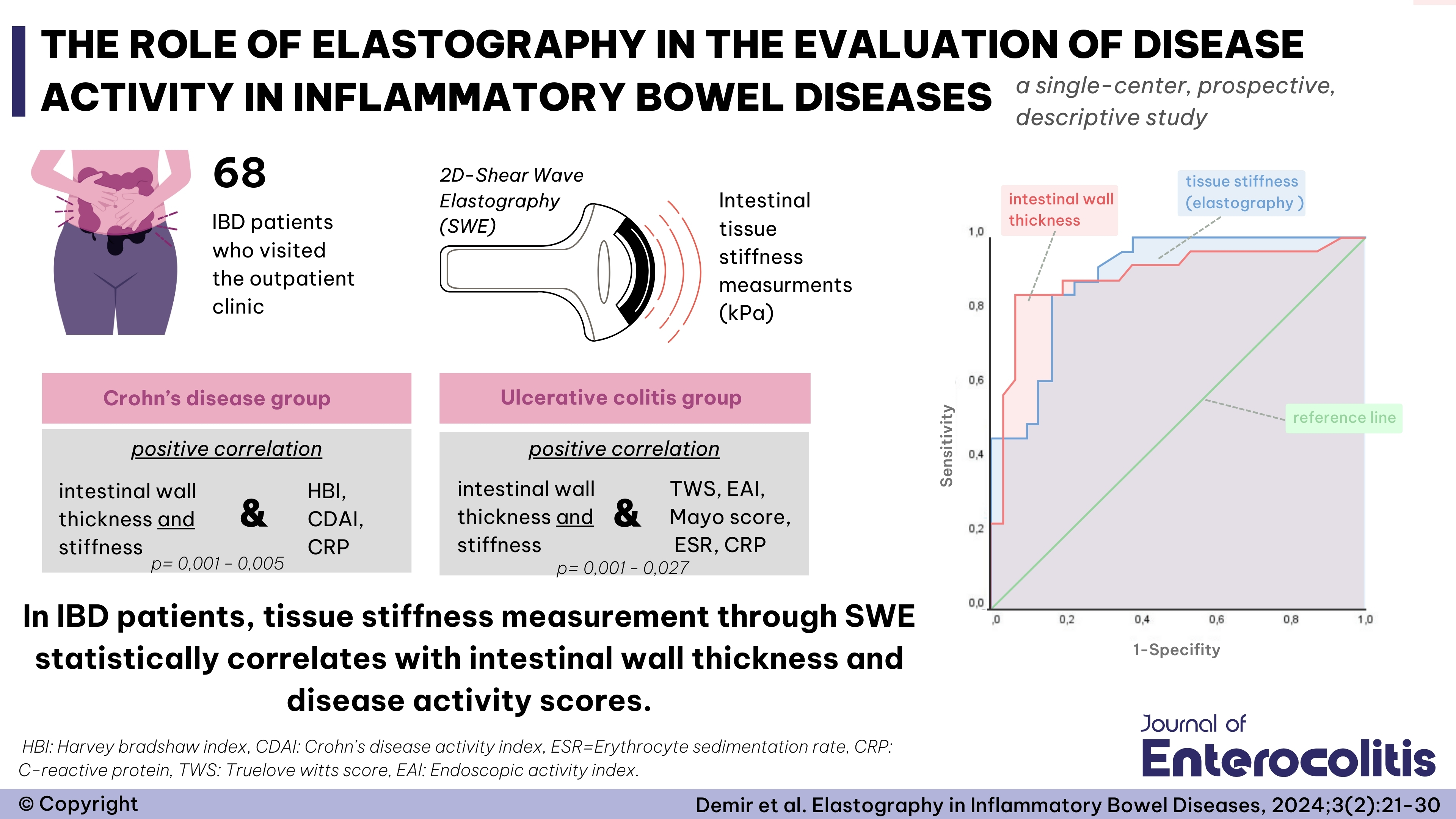


 Tugce Eskazan1
Tugce Eskazan1